





|
|
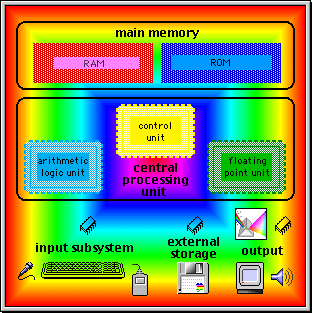
 | Basics of computer hardware:
 | Computer is a programmable machine (or more
precisely, a programmable sequential state machine). There
are two basic kinds of computers: analog and digital. |
 | Analog computers are analog devices. That is, they have
continuous states rather than discrete numbered states. An analog
computer can represent fractional or irrational values exactly, with
no round-off. Analog computers are almost never used outside of
experimental settings. |
 | A digital computer is a programmable clocked sequential
state machine. A digital computer uses discrete states. A binary
digital computer uses two discrete states, such as
positive/negative, high/low, on/off, used to represent the binary
digits zero and one. |
|
 |
Computers are
used for a wide variety of purposes:
 | Data processing is commercial and financial work. This
includes such things as billing, shipping and receiving, inventory
control, and similar business related functions, as well as the
“electronic office”. |
 | Scientific processing is using a computer to support
science. This can be as simple as gathering and analyzing raw data
and as complex as modelling natural phenomenon (weather and climate
models, thermodynamics, nuclear engineering, etc.). |
 | Multimedia includes content creation (composing
music, performing music, recording music, editing film and video,
special effects, animation, illustration, laying out print
materials, etc.) and multimedia playback (games, DVDs, instructional
materials, etc.). |
|
|
|

